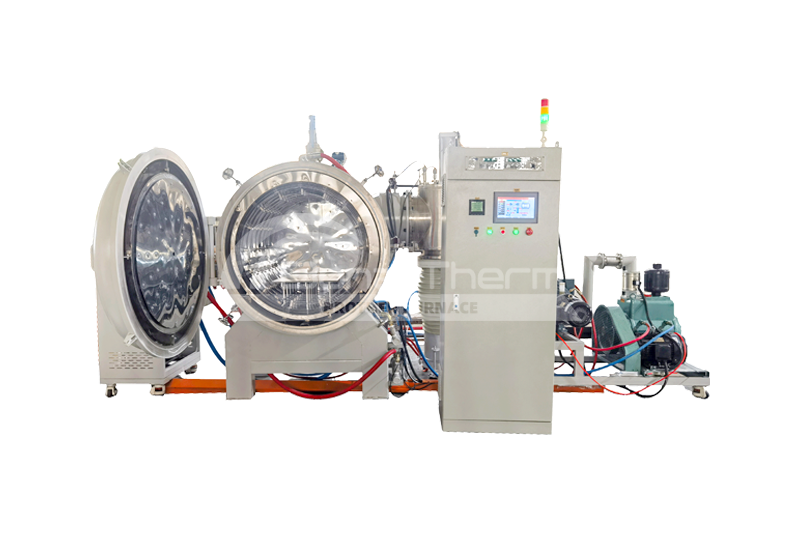
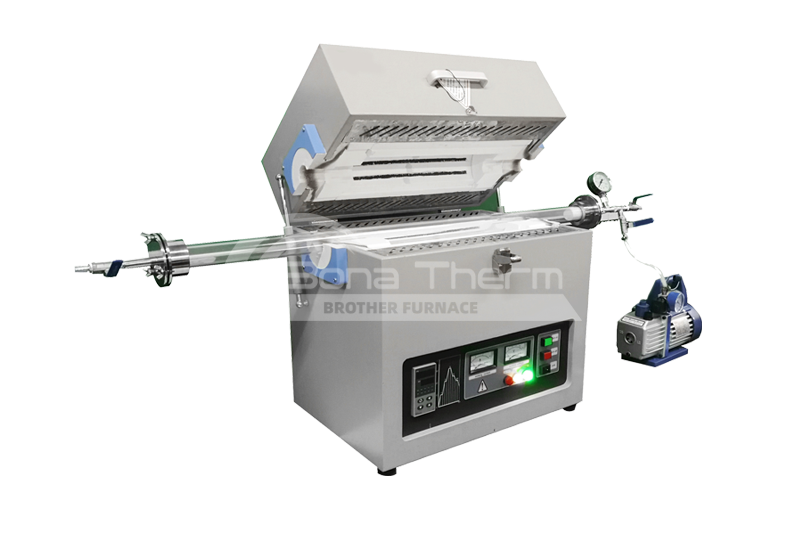
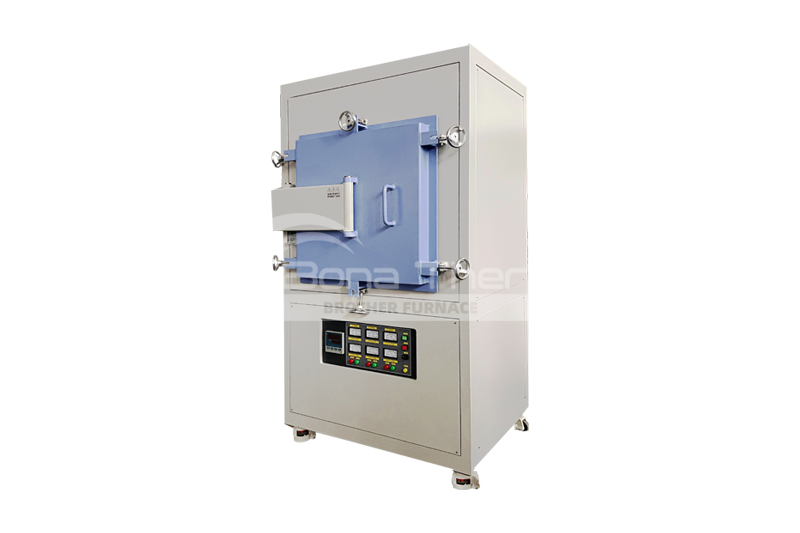
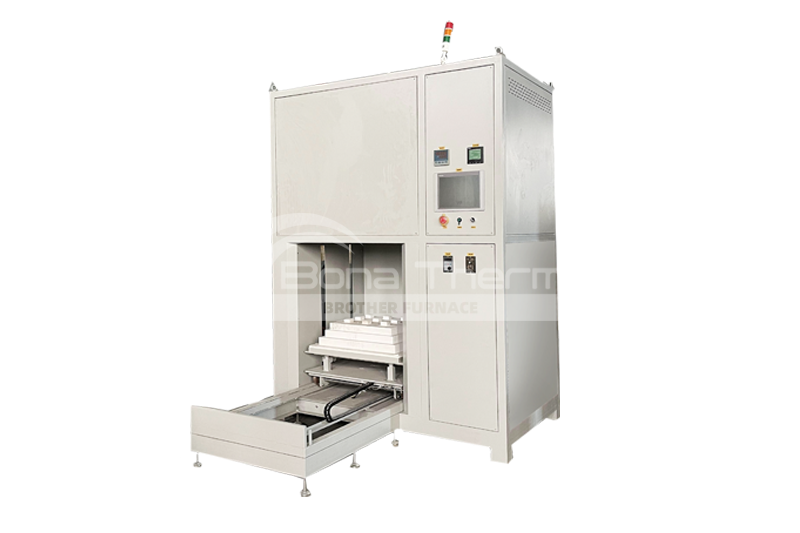
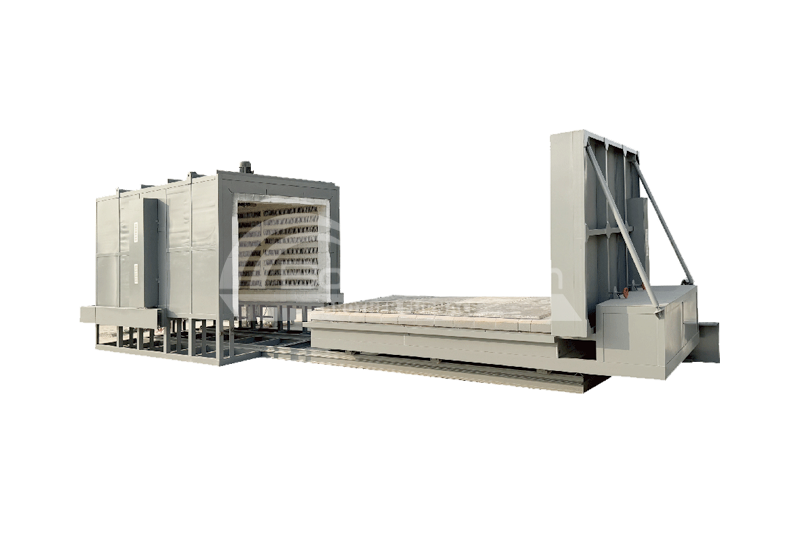
Introduction
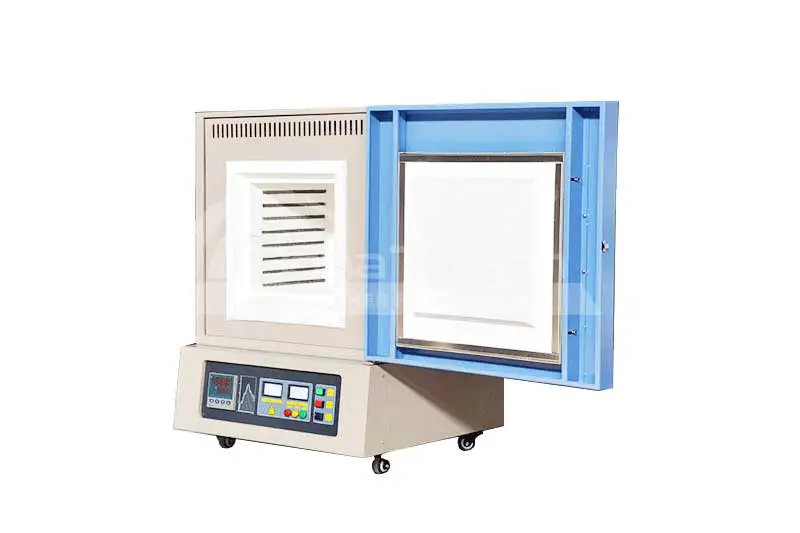
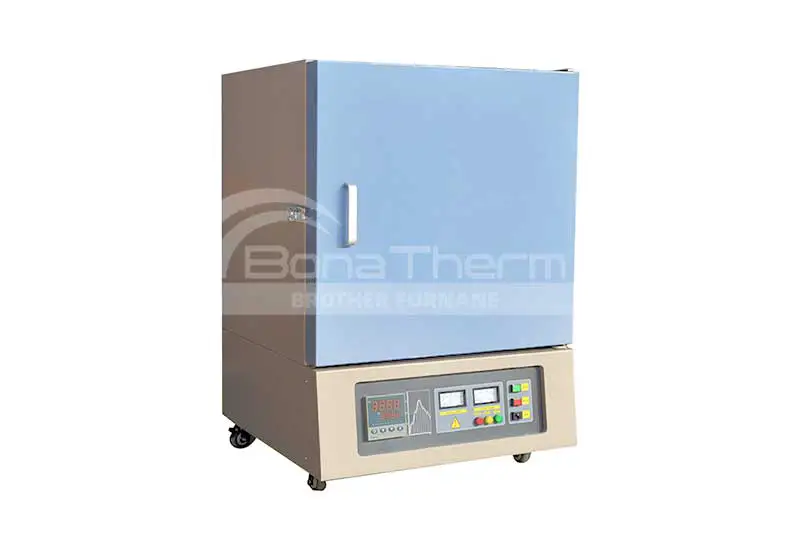
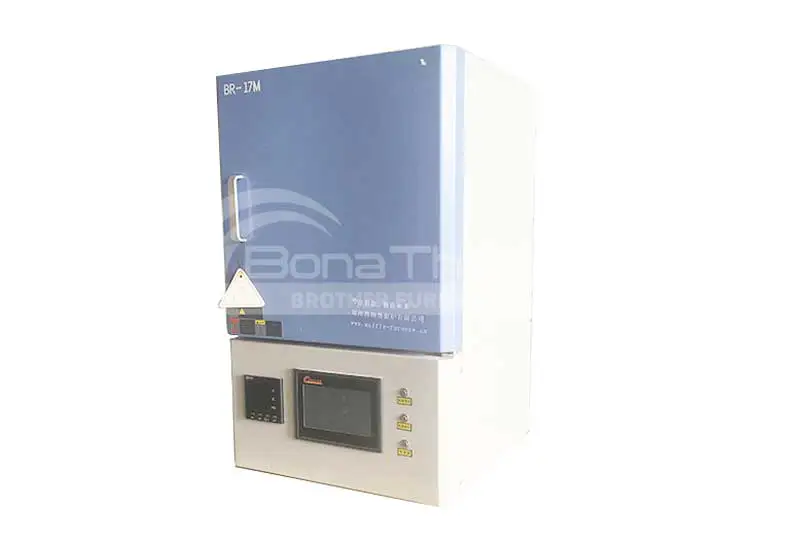
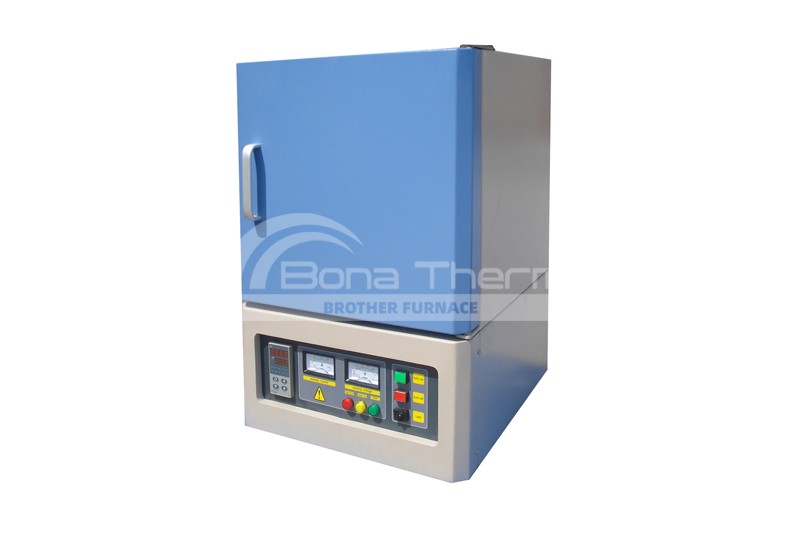
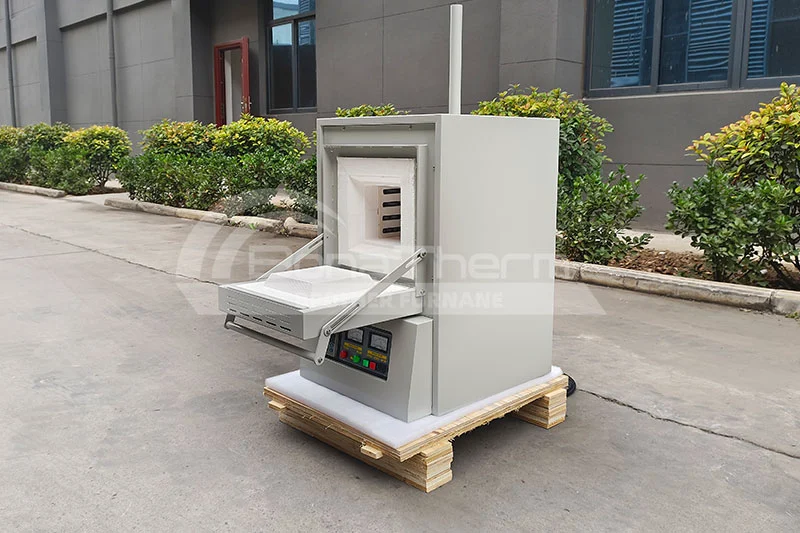
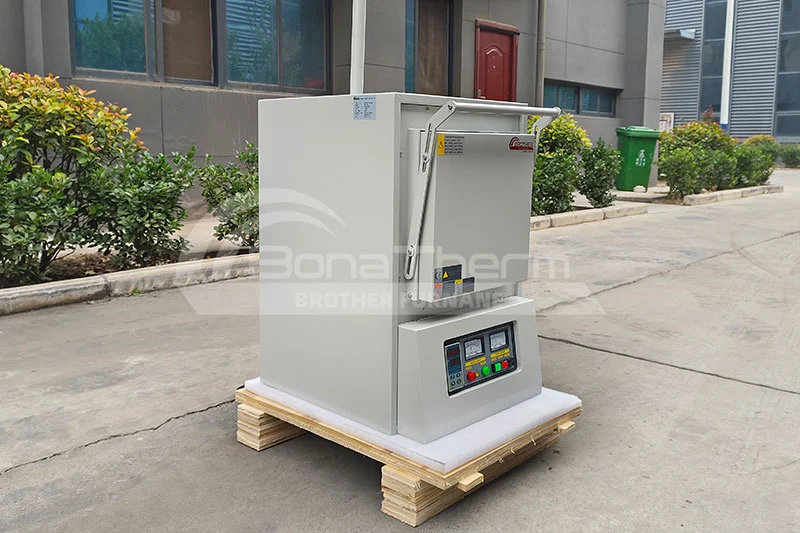
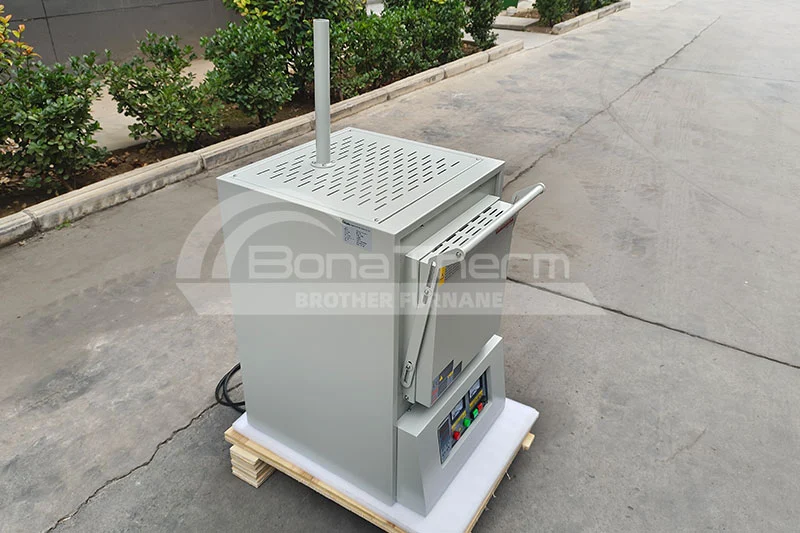
Ashing is the process of heating a sample to remove organic matter from it. This process typically involves subjecting the sample to high temperatures, where the organic material decomposes, leaving behind an inorganic residue known as ash. The purpose of this procedure may be to determine the mass proportion of residual matter (ash) in the sample. In addition, ashing can also be used as an intermediate step in preparing samples for subsequent testing or analysis.
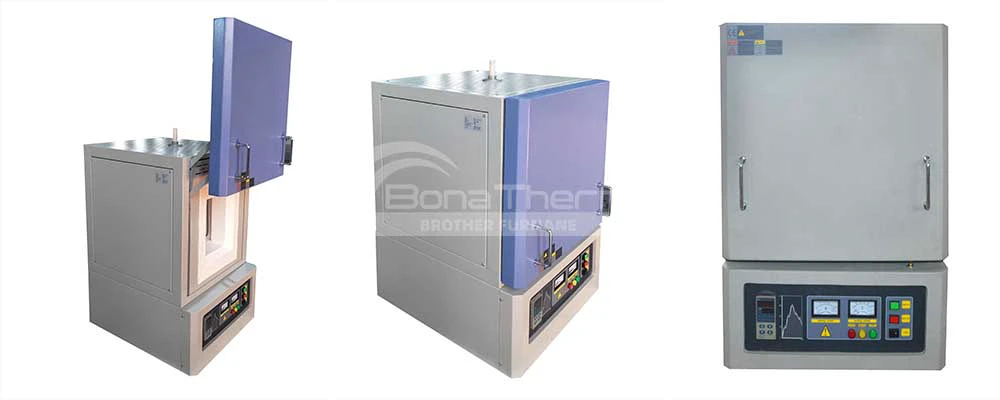

Video of Ashing Furnace
Application
Electronic components
Used for aging tests of electronic components. The high-temperature ashing furnace can simulate the environmental conditions that electronic components may face during long-term use to evaluate their stability and performance.
Plastic chemical products
High-temperature ashing furnace can be used to conduct aging tests on plastic chemical products to help understand the durability and performance of these products under high temperature conditions.
Preheating of knives and iron
Used to preheat tools such as knives and iron to improve their heat treatment properties, such as quenching, burning, stewing, annealing, etc.
Ashing test
High-temperature ashing furnace can be used to conduct ashing test, which is the process of burning out the organic matter in the sample through high temperature, leaving behind ash.
Refining
Under high temperature conditions, it can be used to refine materials to improve their purity and specific properties.
Other high heat treatment tests
Suitable for various high heat treatment tests, including material sintering, alloy processing, etc.






 Get Inquiry
Get Inquiry Send Email
Send Email