Choose Your Vacuum Heat Treatment Sintering Furnace Here
-
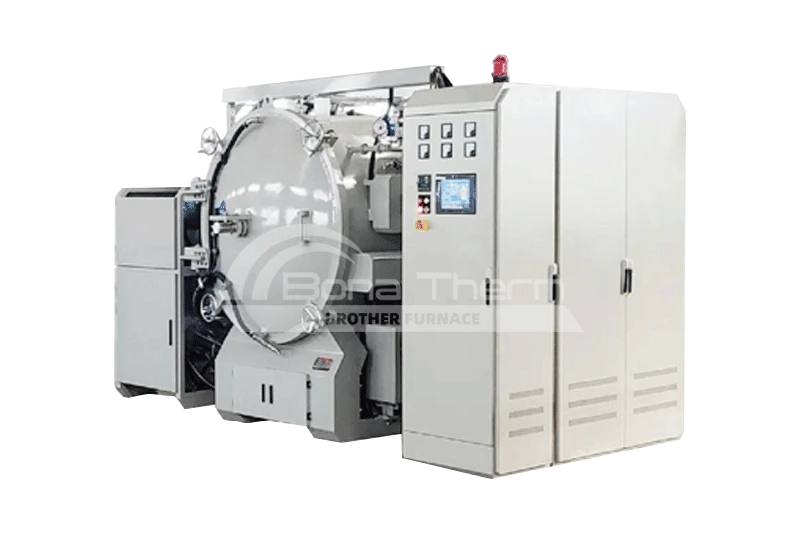

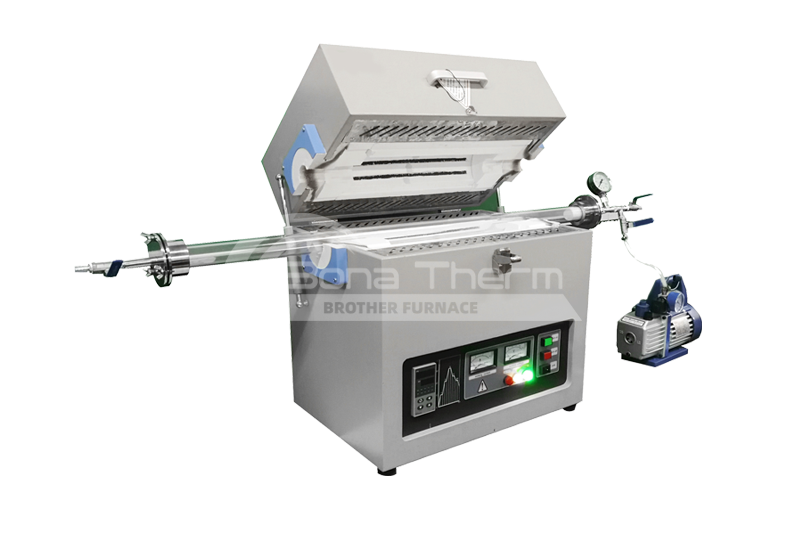
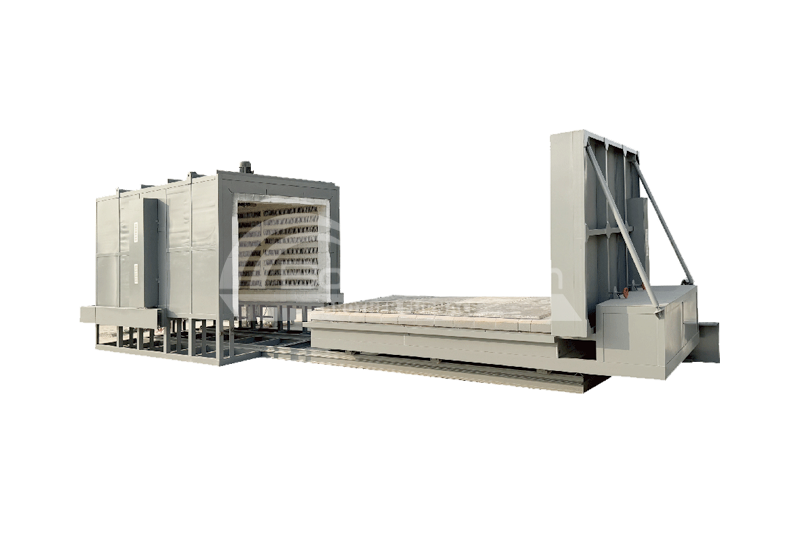
Vacuum Debinding Sintering Furnace
View Products+
-
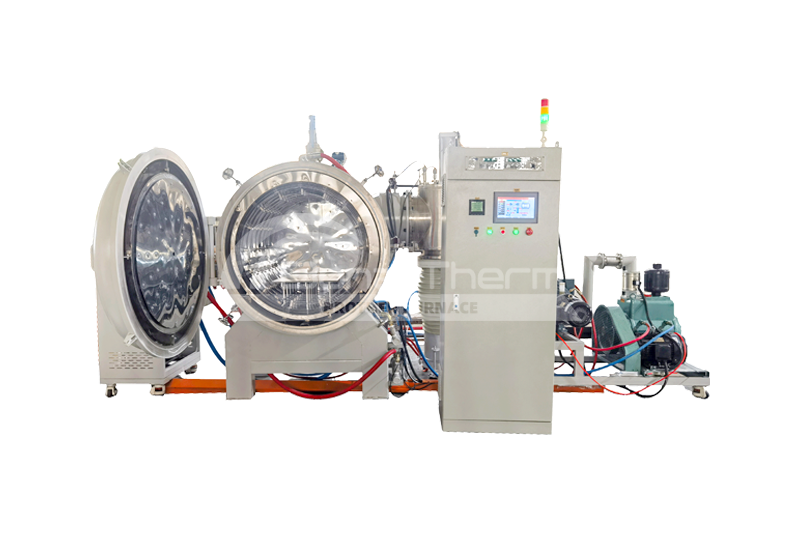

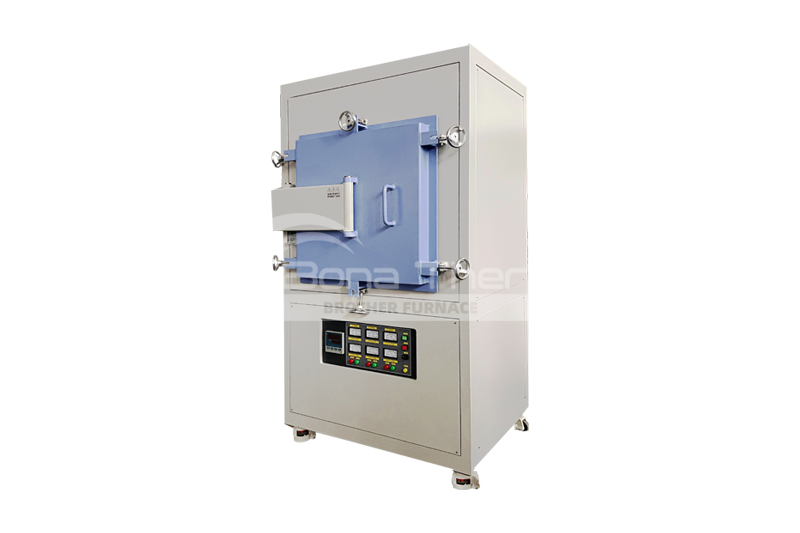
Vacuum Sintering Furnace 1300℃-1500℃( molybdenum thermal field )
View Products+
-
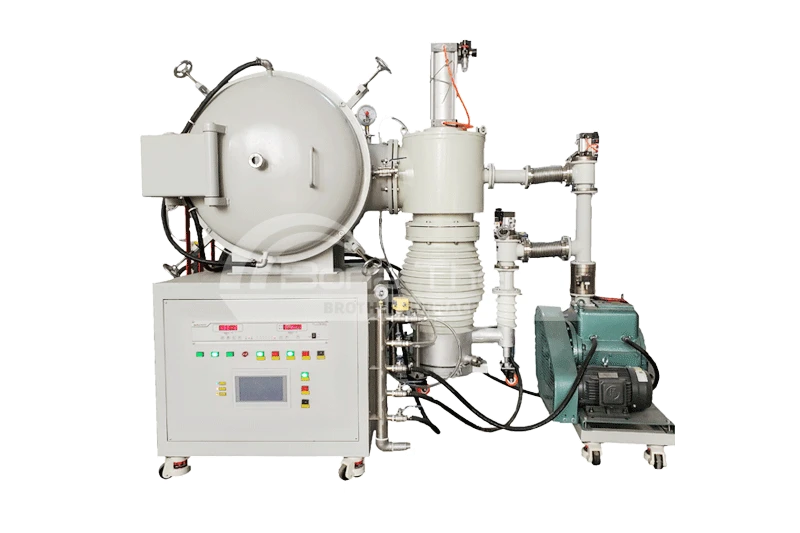
Vacuum Sintering Furnace 1200℃-1700℃( ceramic fiber thermal field )
View Products+
-
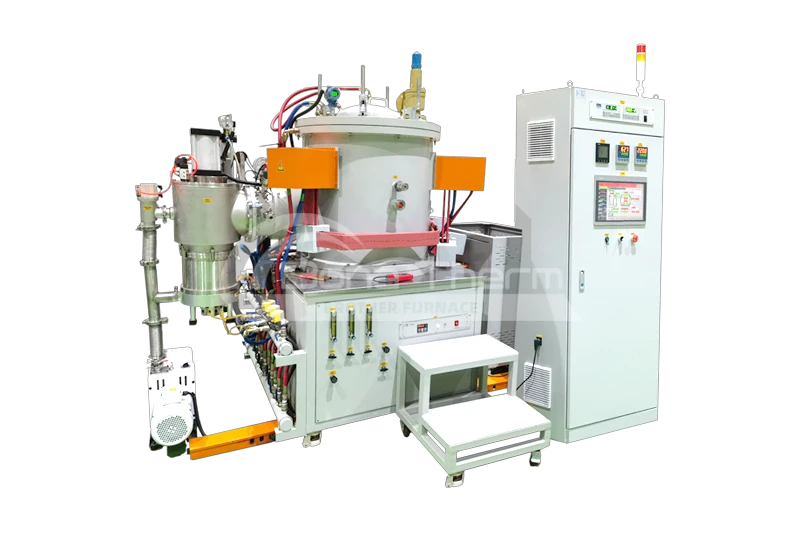

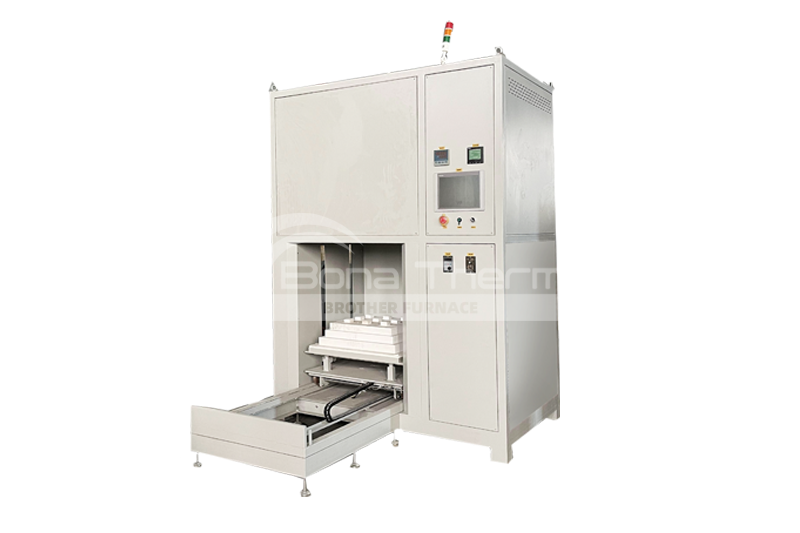
Vacuum Sintering Furnace up to 2300℃(tungsten wire mesh heating)
View Products+
-
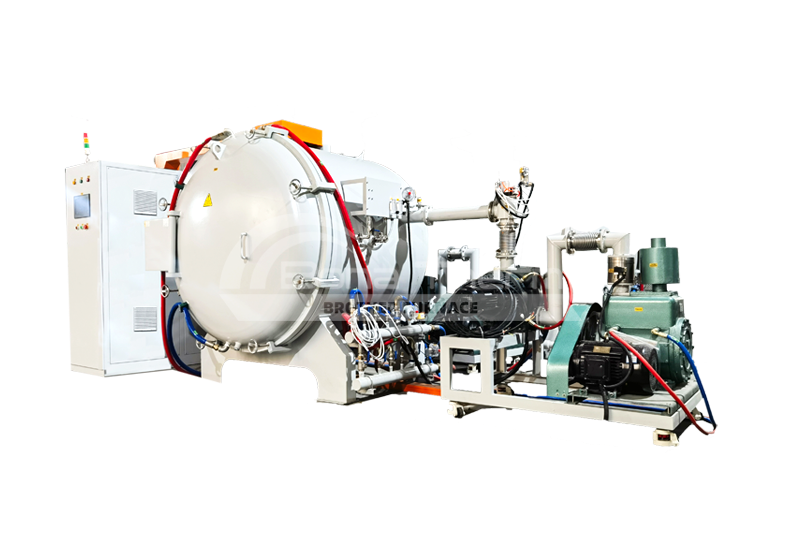
Vacuum Atmosphere Sintering Furnace(inert gas/hydrogen)
View Products+
-
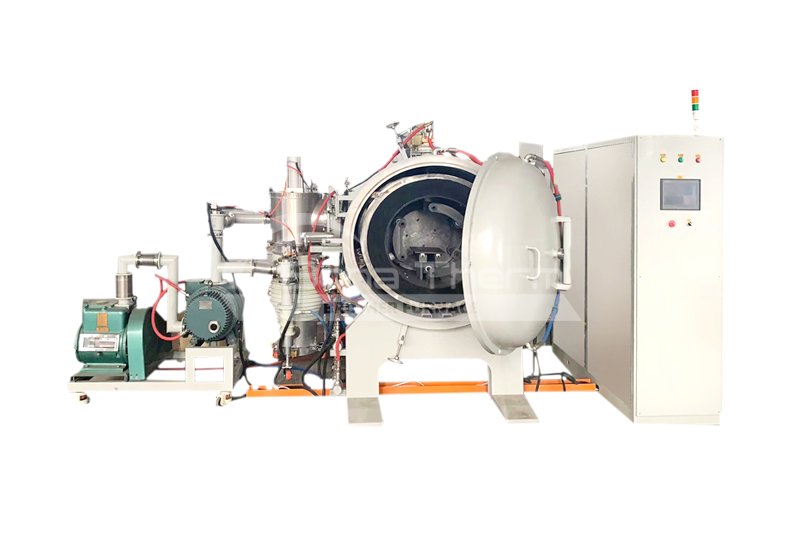
Vacuum Sintering Furnace 1800℃-2200℃(graphite furnace chamber)
View Products+
-
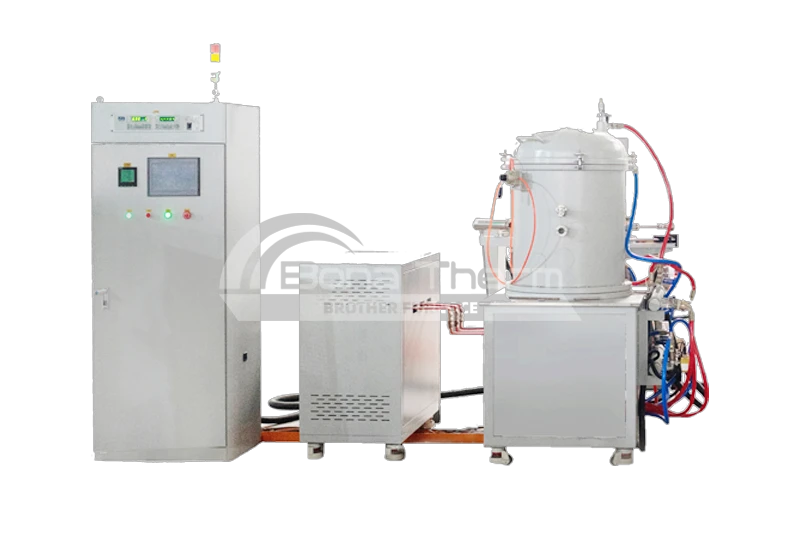

Vacuum Vertical Graphite Carbon Tube Furnace up to 2200℃
View Products+
-

Lithium Hydroxide Vacuum Sintering Furnace
View Products+
Leave message now!
Characteristics of Different Thermal Fields
Thermal Fields Type | Max. Temperature | Core Advantages | Suitable Sintering Materials | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Molybdenum Foil Chamber |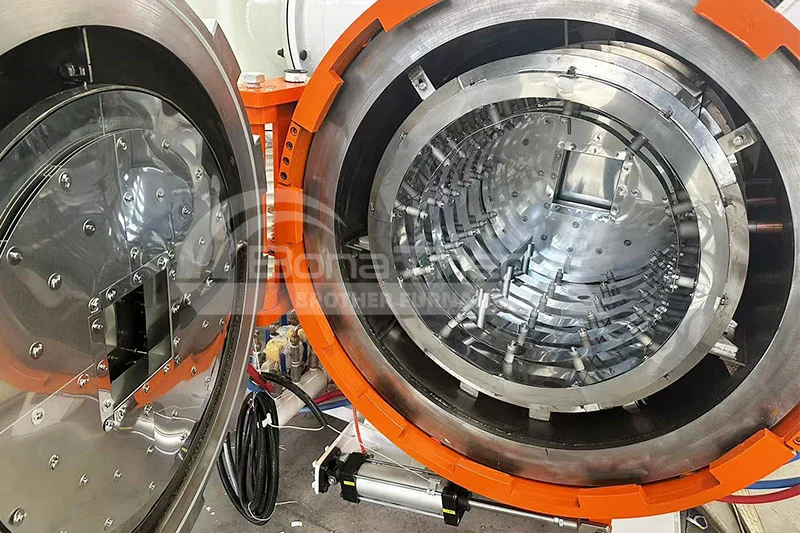  | 1800°C | High strength at elevated temperatures, no contamination | High-temperature alloys (Nickel-based/Cobalt-based), Silicon Carbide (SiC) Ceramics, Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) Ceramics, High-purity metals (Tantalum, Niobium) |
Ceramic Fiber Chamber |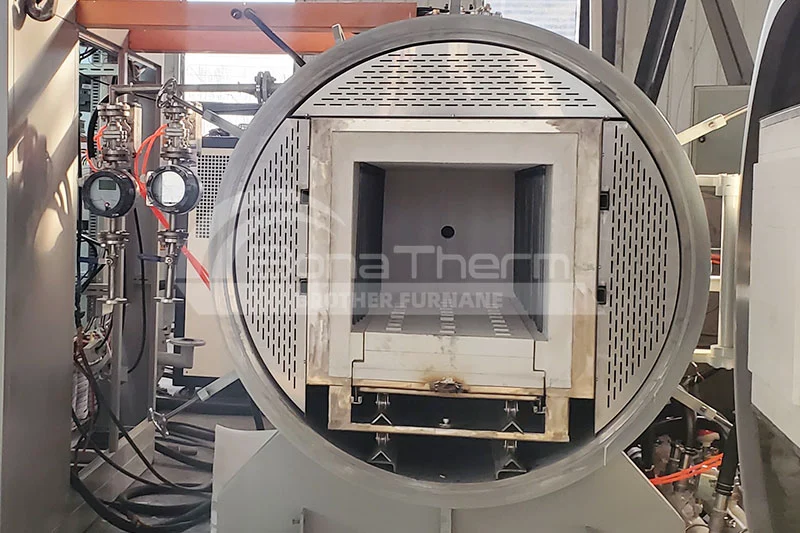  | 1600°C | High strength at elevated temperatures, no contamination | Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramics, Zirconia (ZrO₂) Ceramics, Magnetic Materials (Ferrites), Small-to-medium-sized metal parts (Stainless Steel, Titanium Alloys) |
Tungsten Wire Mesh Chamber |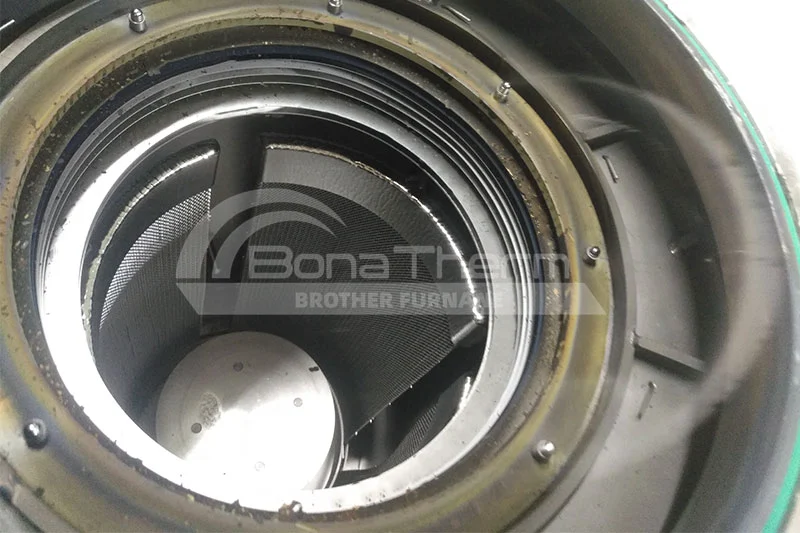  | 2300°C | Extreme high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance | Refractory metals (Tungsten, Molybdenum), Tantalum Carbide (TaC), Boron Nitride (BN), Ultra-high-temperature Ceramics (Zirconium Diboride-Silicon Carbide, ZrB₂-SiC) |
Graphite Chamber |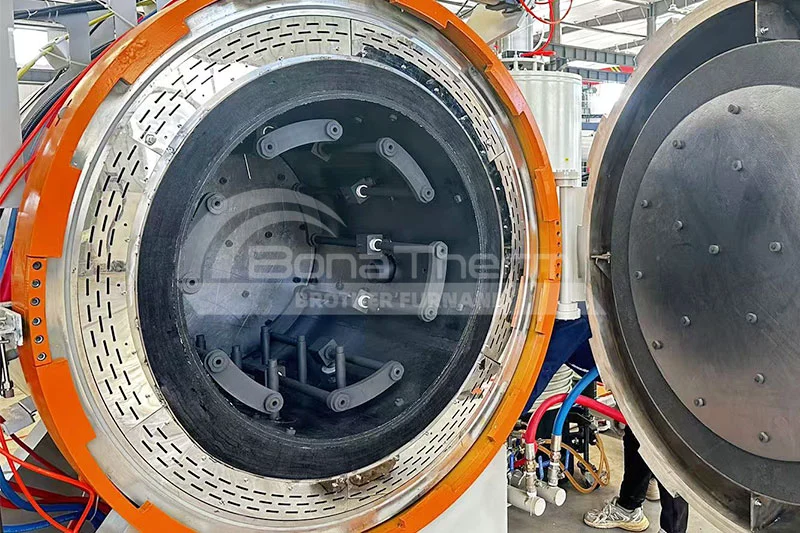  | 2200°C | Ultra-high temperature, cost-effective, thermal shock resistant | Tungsten Carbide (WC), Titanium Carbide (TiC), Graphene Composites, Carbon-Carbon (C/C) Composites |
Heat-resistant Steel Chamber |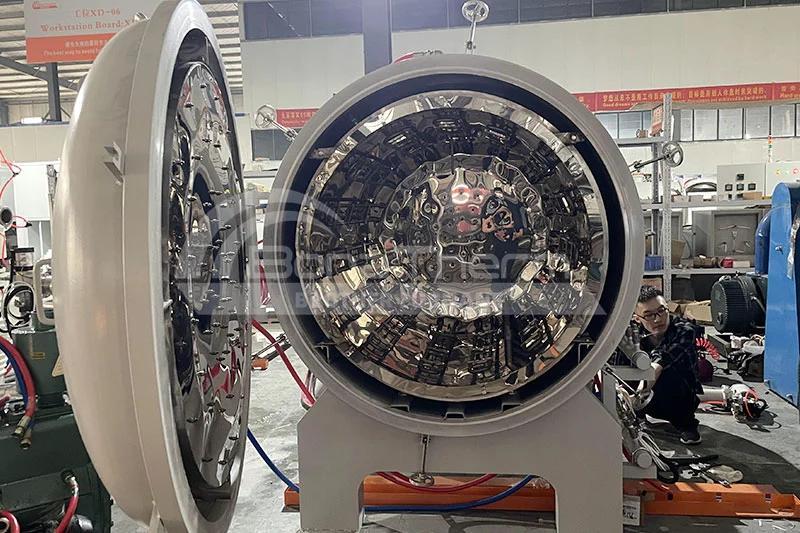  | 1200°C | Corrosion-resistant, easy to process, low cost | Copper-based alloys, Aluminum alloys, Low-melting-point metal powders (Tin, Lead), Magnetic alloys (NdFeB) |
Common Questions of Vacuum Heat Treatment Sintering Furnace
● What are the advantages of sintering in a vacuum environment?
Prevents material oxidation and decarburization, improves sintering density and purity, reduces contamination, enhances mechanical properties, and allows precise atmosphere control for better product consistency.
● What is the temperature range of a vacuum sintering furnace?
Typically ranges from 1200°C to 2500°C, depending on the furnace design and heating elements. Common options include graphite heating and tungsten/molybdenum heating.
● What materials can be sintered in a vacuum furnace?
Suitable for metals (such as tungsten, molybdenum, titanium, stainless steel), ceramics (such as alumina, silicon nitride), hard alloys, magnetic materials (such as NdFeB), composite materials, and powder metallurgy components.
● Can a vacuum sintering furnace introduce gases?
Yes, commonly used gases include argon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. These gases serve different purposes, such as providing a protective atmosphere, acting as a reducing agent, or optimizing the sintering environment. For example, hydrogen helps reduce oxidation and improve sintering quality.
● How to choose the right furnace?
To meet specific process needs, consider factors such as material type, maximum temperature, vacuum level, atmosphere control, chamber size, production capacity, and automation requirements.